Cells, tissues and organs -> acceleration
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate at which an object changes its velocity. It can occur when an object speeds up, slows down, or changes direction. The formula for acceleration is:
Acceleration = (Change in velocity) / (Time taken)
Acceleration is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. This means that an object can accelerate by changing its speed, its direction, or both. Acceleration is measured in units of distance per time squared, such as meters per second squared (m/s^2).
Types of Acceleration
There are several types of acceleration:
- Positive Acceleration: This occurs when an object's velocity increases over time, such as when a car speeds up.
- Negative Acceleration (Deceleration): This occurs when an object's velocity decreases over time, such as when a car slows down or comes to a stop.
- Uniform Acceleration: This occurs when an object's velocity changes by the same amount in each equal time period.
- Non-uniform Acceleration: This occurs when an object's velocity changes by different amounts in each equal time period.
Factors Affecting Acceleration
Several factors can affect the acceleration of an object:
- Force: The application of force can cause an object to accelerate, following Newton's second law of motion (F = ma).
- Mass: Heavier objects require more force to accelerate compared to lighter objects, as described by Newton's second law (F = ma).
- Friction: The presence of frictional forces can oppose an object's motion, affecting its acceleration.
- Gravity: The force of gravity can cause objects to accelerate towards the Earth at a rate of 9.8 m/s^2.
Examples of Acceleration
Some common examples of acceleration include:
- A car speeding up or slowing down
- An object falling towards the Earth due to gravity
- A rocket launching into space
- A pendulum swinging back and forth
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember about acceleration:
- Acceleration is the rate at which an object changes its velocity.
- It can be positive, negative, uniform, or non-uniform.
- Acceleration is a vector quantity with both magnitude and direction.
- Factors affecting acceleration include force, mass, friction, and gravity.
- Acceleration can be calculated using the formula: Acceleration = (Change in velocity) / (Time taken)
Understanding acceleration is crucial in many scientific and engineering fields, especially in the study of motion and forces.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fifth Grade. Cells, tissues and organs

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key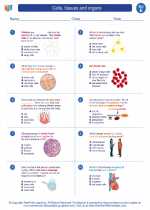
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key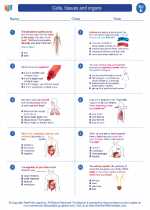
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
