Newton's Second Law of Motion
Newton's Second Law of Motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. This can be represented by the formula:
center;">F = ma
Where:
- F = net force acting on the object (in Newtons)
- m = mass of the object (in kilograms)
- a = acceleration of the object (in meters per second squared)
This means that the greater the force applied to an object, the greater its acceleration will be. Similarly, the greater the mass of an object, the smaller its acceleration will be for the same amount of force applied.
Study Guide
- What is the formula for Newton's Second Law of Motion?
- What does each variable in the formula represent?
- How is acceleration related to force and mass according to Newton's Second Law?
F = ma
F = net force acting on the object (in Newtons)
m = mass of the object (in kilograms)
a = acceleration of the object (in meters per second squared)
Acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to its mass.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Genetics - Study of Heredity
Study Guide Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson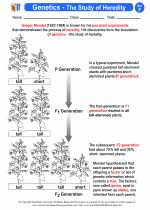 Genetics - The Study of Heredity
Genetics - The Study of Heredity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Genetics - Study of Heredity
Genetics - Study of Heredity 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
LIFE SCIENCE
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for how environmental and genetic factors influence the growth of organisms.
Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of Traits