Genetics - Study of Heredity -> tissues
Tissues
Tissues are groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function in the body. There are four main types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue.
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue covers the body's surfaces and lines its cavities. It serves as a protective barrier and helps with absorption and secretion. Examples include the outer layer of the skin and the lining of the digestive tract.
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue provides support and connects different body parts. It includes a wide variety of structures such as bone, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and blood. Connective tissue also plays a role in defending the body against infection and storing energy in the form of fat.
Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue is responsible for movement. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and allows for voluntary movements, while cardiac muscle forms the heart and is responsible for pumping blood. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of internal organs and controls involuntary movements.
Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and supporting cells. It conducts electrical impulses and is the main component of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Nervous tissue enables the body to receive stimuli from the environment, process information, and coordinate responses.
Study Guide
When studying tissues, it's important to understand the following key points:
- The structure and function of each type of tissue.
- Examples of where each type of tissue is found in the body.
- The different types of cells and extracellular matrix components that make up each tissue.
- The roles of tissues in maintaining homeostasis and supporting overall body function.
- The importance of tissues in the context of human anatomy and physiology.
Additionally, it's helpful to use visual aids such as diagrams and histological slides to identify and understand the different types of tissues under a microscope.
Understanding tissues is crucial for comprehending how the human body functions at a cellular and structural level. Mastery of this topic will provide a solid foundation for further studies in biology, anatomy, and physiology.
[Tissues] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Genetics - Study of Heredity

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson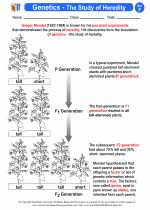
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
