Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells are characterized by the presence of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells, which do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells
- Nucleus: Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus that houses the genetic material (DNA) in the form of chromosomes.
- Membrane-bound Organelles: Eukaryotic cells contain various membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and chloroplasts (in plant cells).
- Complex Structure: Eukaryotic cells have a more complex internal structure compared to prokaryotic cells.
- Cytoskeleton: Eukaryotic cells have a network of protein filaments known as the cytoskeleton, which provides structural support and helps in cell movement.
- Cell Division: Eukaryotic cells undergo a process called mitosis for somatic cell division and meiosis for reproductive cell division.
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells contain various organelles that perform specific functions within the cell:
- Mitochondria: Site of cellular respiration and energy production.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
- Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion.
- Lysosomes: Contain digestive enzymes for breaking down waste materials.
- Chloroplasts: Found in plant cells and are the site of photosynthesis.
Study Guide
When studying eukaryotic cells, it's important to focus on the following key points:
- Understand the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
- Memorize the functions of the major organelles within eukaryotic cells.
- Be able to identify and label the organelles in a eukaryotic cell diagram.
- Learn about the processes of mitosis and meiosis in eukaryotic cells.
By mastering these concepts, you'll have a solid understanding of eukaryotic cells and their significance in biological systems.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Introduction to earth science
Study Guide Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson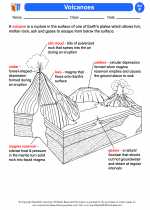 Volcanoes
Volcanoes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE