What is Exocytosis?
Exocytosis is the process by which cells release molecules or particles from inside the cell to the outside through fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane.Steps of Exocytosis
- Vesicle Formation: Molecules to be transported are packaged into vesicles within the cell.
- Vesicle Transport: The vesicles move towards the plasma membrane along the cytoskeleton.
- Membrane Fusion: The vesicle membrane fuses with the plasma membrane, releasing the vesicle contents into the extracellular space.
- Membrane Recycling: The plasma membrane is recycled to maintain cell surface area after exocytosis.
Types of Exocytosis
There are two main types of exocytosis:- Constitutive Exocytosis: Continuous, unregulated release of vesicle contents, such as the secretion of mucus by goblet cells.
- Regulated Exocytosis: Triggered release of vesicle contents in response to specific signals, such as the release of neurotransmitters by nerve cells.
Role of Exocytosis in Cells
Exocytosis serves several important functions in cells:- Neurotransmitter Release: Allows nerve cells to communicate with each other and with muscles.
- Hormone Secretion: Enables endocrine cells to release hormones into the bloodstream.
- Waste Removal: Facilitates the removal of waste materials from the cell.
- Cell Growth and Repair: Contributes to the expansion of the cell surface area during growth and repair processes.
Factors Affecting Exocytosis
Exocytosis can be influenced by various factors, including:- Intracellular Signaling: Cellular signals that trigger or regulate exocytosis.
- Cytoskeletal Dynamics: The movement of vesicles along the cytoskeleton towards the plasma membrane.
- Membrane Composition: The lipid and protein composition of the plasma membrane can affect the process of membrane fusion.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Introduction to earth science
Study Guide Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson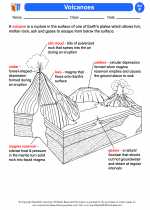 Volcanoes
Volcanoes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE