Gamma Rays
Gamma rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, which are high-energy photons. They have the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays are produced by the decay of radioactive atoms and during nuclear reactions.
Here's a study guide for understanding gamma rays:
- Properties: Gamma rays have no mass or charge and are highly penetrating, meaning they can pass through most materials. They are the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation.
- Sources: Gamma rays are emitted from the nuclei of radioactive atoms as they undergo radioactive decay. They are also produced during nuclear reactions such as those that occur in stars or during nuclear power generation.
- Uses: Gamma rays have various applications including medical imaging (gamma-ray cameras), cancer treatment (radiation therapy), sterilization of medical equipment, and in industrial processes such as material testing and imaging of pipelines.
- Effects: Exposure to high doses of gamma rays can be harmful and can cause damage to living tissues. However, controlled exposure is used in medical treatments and other applications.
- Protection: Lead and concrete are commonly used to shield against gamma rays due to their high density and ability to absorb the radiation.
Understanding gamma rays and their properties is important in various scientific and technological fields. It also sheds light on the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic levels.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Introduction to earth science
Study Guide Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson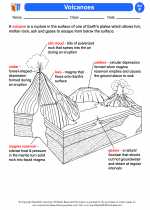 Volcanoes
Volcanoes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE