Properties of Glass
- Transparency: Glass is transparent, allowing light to pass through it, making it suitable for windows and lenses.
- Hardness: While glass is relatively hard, it can also be brittle and prone to shattering under stress.
- Chemical Inertness: Glass is resistant to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for storing liquids and chemicals.
- Thermal Insulation: It is a poor conductor of heat, making it suitable for insulating buildings and as a thermal barrier.
- Electrical Insulation: Glass is an excellent electrical insulator, making it useful in electronics and power transmission.
Types of Glass
- Soda-Lime Glass: The most common type used in windows, containers, and light bulbs.
- Borosilicate Glass: Known for its resistance to thermal expansion and used in laboratory glassware and cookware.
- Tempered Glass: Treated for increased strength and used in applications requiring safety glass, such as car windows and shower doors.
- Fiberglass: Made from fine fibers of glass and used in insulation, composites, and textiles.
- Optical Glass: Engineered for its optical properties and used in lenses, prisms, and fiber optics.
Studying Glass
When studying glass, it's important to understand its composition, properties, and various uses.
- Chemical Composition: The primary components of glass are silica (silicon dioxide), soda ash (sodium carbonate), and lime (calcium oxide).
- Manufacturing Processes: Learning about the different methods of producing glass, such as float glass, blown glass, and cast glass, provides insight into the diversity of glass products.
- Applications: Exploring the wide range of applications for glass, from architectural uses to specialized technical applications, helps to appreciate its versatility.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Introduction to earth science
Study Guide Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson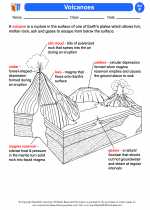 Volcanoes
Volcanoes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE