Habitat
A habitat is the natural environment in which an organism (plant or animal) lives and thrives. It provides the necessary resources such as food, water, shelter, and space for the organism to survive. Habitats can be as small as a puddle or as large as an ocean, and they can be found on land, in water, or even in the air.
Components of a Habitat:
- Food: Organisms depend on the availability of food in their habitat. Some organisms are herbivores, feeding on plants, while others are carnivores, feeding on other animals.
- Water: All living organisms require water to survive. Habitats that lack water may not be suitable for certain species.
- Shelter: Shelter provides protection from weather, predators, and other threats. It can be in the form of burrows, nests, or even the physical features of the habitat itself.
- Space: Sufficient space is necessary for organisms to carry out their activities such as hunting, nesting, and breeding.
Types of Habitats:
Habitats can be classified into various types based on the physical and biological characteristics. Some common types of habitats include:
- Terrestrial Habitats: These include habitats on land such as forests, grasslands, deserts, and tundra.
- Aquatic Habitats: These include habitats in water bodies such as oceans, rivers, lakes, and ponds.
- Amphibious Habitats: These are transitional habitats, such as wetlands, that are a mix of terrestrial and aquatic environments.
- Aerial Habitats: These habitats are found in the air, such as the canopy of trees or the open sky for birds and insects.
Adaptations to Habitats:
Organisms have evolved various physical and behavioral adaptations to survive in their specific habitats. These adaptations can include camouflage, migration, hibernation, and specialized body structures.
Importance of Habitats:
Habitats are essential for the survival of living organisms and play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. They provide biodiversity, contribute to ecological processes, and offer valuable resources for human use.
Study Guide Questions:
- What is a habitat and why is it important for organisms?
- List and describe the components of a habitat.
- Explain the different types of habitats with examples.
- How do organisms adapt to their specific habitats?
- Discuss the significance of habitats in maintaining ecological balance.
Understanding habitats is crucial for comprehending the interactions between organisms and their environment. It forms the basis for ecological studies and conservation efforts to preserve the diversity of life on Earth.
[Habitat] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson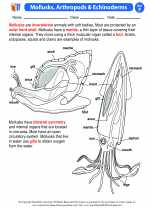
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
