Anatomy of the Kidneys
- Location: The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine, just below the rib cage.
- Structure: Each kidney is made up of an outer cortex and inner medulla, containing millions of nephrons, the functional units of the kidneys.
- Nephrons: These are the filtering units of the kidneys, consisting of a glomerulus (a cluster of blood vessels) and a renal tubule.
- Renal Artery and Vein: Blood is supplied to the kidneys through the renal artery and drained by the renal vein.
Functions of the Kidneys
- Filtration: The kidneys filter waste products, toxins, and excess substances from the blood to produce urine.
- Regulation of Fluid Balance: The kidneys help maintain the body's water balance by adjusting the volume and concentration of urine produced.
- Regulation of Blood Pressure: They produce the hormone renin, which helps regulate blood pressure and maintain proper blood volume.
- Acid-Base Balance: The kidneys help regulate the body's acid-base balance by excreting hydrogen ions and reabsorbing bicarbonate ions.
- Production of Erythropoietin: Erythropoietin, a hormone produced by the kidneys, stimulates the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow.
Common Kidney Disorders
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): A condition in which the kidneys gradually lose function over time, often leading to end-stage renal disease.
- Kidney Stones: Hard deposits of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys and can cause severe pain when passing through the urinary tract.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Infections that can affect the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, leading to symptoms such as pain, frequency, and urgency of urination.
- Acute Kidney Injury: Sudden loss of kidney function due to various factors such as dehydration, severe infection, or medication toxicity.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Study Guide Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson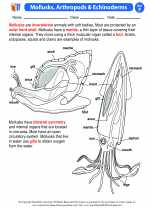 Mollusks, Arthropods & Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods & Echinoderms  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
LIFE SCIENCE
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes