Latitude
Latitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is measured in degrees north or south of the equator, which is designated as 0 degrees latitude.
Key Concepts
- Equator: The equator is an imaginary line that circles the Earth halfway between the North Pole and the South Pole. It is designated as 0 degrees latitude.
- Measurement: Latitude is measured in degrees, with the equator being 0 degrees, the North Pole being 90 degrees north, and the South Pole being 90 degrees south.
- Lines of Latitude: Lines of latitude run parallel to the equator and are used to specify the north-south position of a location on Earth.
- Climate: Latitude plays a crucial role in determining climate patterns, as areas closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight and tend to be warmer, while areas closer to the poles receive less direct sunlight and tend to be colder.
Study Guide
When studying latitude, it's important to understand the following:
- What is latitude and how is it measured?
- Why is the equator designated as 0 degrees latitude?
- How do lines of latitude help in locating places on Earth?
- How does latitude influence climate patterns?
Additionally, it's helpful to practice locating and identifying the latitudinal position of different cities and geographic features on a world map.
[Latitude] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Study Guide Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson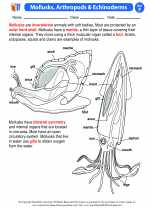 Mollusks, Arthropods & Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods & Echinoderms  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
LIFE SCIENCE
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes