Longitudinal Waves
Longitudinal waves are a type of mechanical wave in which the disturbance of the medium is in the same direction as the motion of the wave. This means that the particles of the medium move parallel to the direction of the wave. Sound waves are a common example of longitudinal waves.
Key Concepts
- Particle Motion: In longitudinal waves, the particles of the medium move back and forth in the same direction as the wave.
- Compression and Rarefaction: Longitudinal waves have regions of high density called compressions and regions of low density called rarefactions.
- Propagation: Longitudinal waves can travel through solids, liquids, and gases.
- Examples: Sound waves, seismic waves, and waves in springs are all examples of longitudinal waves.
Study Guide
When studying longitudinal waves, it's important to understand the following key points:
- Describe how the particles of the medium move in a longitudinal wave.
- Explain the concept of compression and rarefaction in longitudinal waves.
- Discuss the propagation of longitudinal waves through different mediums.
- Provide real-life examples of longitudinal waves and their applications.
Be sure to review the properties of longitudinal waves and practice identifying them in different contexts to solidify your understanding of this important wave phenomenon.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Study Guide Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson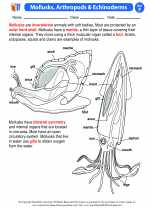 Mollusks, Arthropods & Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods & Echinoderms  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms
Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
LIFE SCIENCE
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes