Margins
In the context of science, margins refer to the edge or border of a surface or structure. This concept is important in various scientific fields such as geography, biology, and geology.
Geography
In geography, margins are often used to describe the edge of a landform or a body of water. For example, the coastline is the margin between the land and the ocean. Understanding the margins of different geographical features helps geographers analyze ecosystems and human settlements.
Biology
In biology, margins are significant in the study of plant and animal anatomy. The margin of a leaf, for instance, refers to the edge or boundary of the leaf. Examining leaf margins can provide insight into the species of the plant and its adaptations to its environment.
Geology
In geology, margins are crucial in the study of tectonic plate boundaries. The margins of tectonic plates can be convergent, divergent, or transform, and these different types of plate margins are associated with specific geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the formation of mountain ranges.
Study Guide for Margins
- Define Margins: Describe what margins are and provide examples from different scientific fields.
- Geographical Margins: Explain the significance of understanding geographical margins and provide examples of how they impact ecosystems and human societies.
- Biological Margins: Discuss the importance of studying margins in biology, particularly in relation to plant and animal anatomy and adaptations.
- Geological Margins: Explore the role of margins in geology, focusing on tectonic plate boundaries and their impact on Earth's surface and natural phenomena.
- Real-World Applications: Research and present real-world examples of how an understanding of margins has contributed to scientific discoveries or practical applications in fields such as conservation, agriculture, or urban planning.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson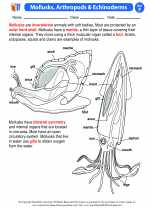
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
