Underground Aquifers
An underground aquifer is a layer of permeable rock or sediment that holds water and allows it to flow. These aquifers are a crucial source of fresh water for human consumption, agriculture, and industry. Understanding the properties and dynamics of underground aquifers is essential for sustainable water management.
Formation of Underground Aquifers
Underground aquifers are formed when water from precipitation or surface water sources percolates through the ground and gets stored in porous rock layers such as sandstone, gravel, or fractured rocks. The water is held in the spaces between the particles or within the fractures, creating a reservoir of groundwater.
Characteristics of Aquifers
Aquifers can be confined or unconfined. A confined aquifer is located between two impermeable layers of rock, which prevent the water from moving vertically. An unconfined aquifer, on the other hand, has no impermeable layers above it, allowing water to move freely in and out of the aquifer.
The porosity and permeability of the rock or sediment determine the storage and movement of water within the aquifer. Porosity refers to the volume of open spaces within the rock, while permeability describes the ability of the rock to transmit water. Highly porous and permeable materials, such as sandstone, make good aquifers as they can store and transmit large quantities of water.
Recharge and Discharge of Aquifers
Aquifers are recharged through the infiltration of precipitation or surface water. This replenishes the groundwater reservoir and sustains the flow of water within the aquifer. The rate of recharge depends on factors such as the type of soil or rock, the amount of precipitation, and human activities such as irrigation and land use.
Discharge occurs when groundwater flows out of the aquifer through natural springs, seeps into rivers and lakes, or is extracted through wells for human use. Understanding the balance between recharge and discharge is crucial for maintaining the sustainability of underground aquifers.
Study Guide Questions
- What is an underground aquifer and how is it formed?
- Explain the difference between confined and unconfined aquifers.
- Describe the importance of porosity and permeability in aquifers.
- Discuss the processes of recharge and discharge in underground aquifers.
- How can human activities impact the sustainability of aquifers?
Understanding the dynamics of underground aquifers is vital for ensuring a sustainable supply of fresh water for current and future generations. It also plays a crucial role in environmental conservation and ecosystem health.
[Underground Aquifers] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Mollusks, Arthropods and Echinoderms

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson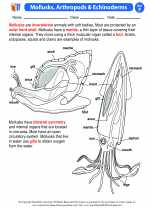
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
