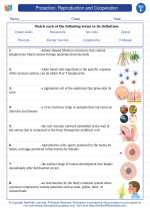
Biogas: An Overview
Biogas is a renewable energy source produced by the anaerobic digestion of organic materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, and sewage. It is composed primarily of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), with small amounts of other gases such as hydrogen sulfide and water vapor.
How Biogas is Produced
The production of biogas occurs through a natural process called anaerobic digestion, which takes place in an oxygen-free environment. During anaerobic digestion, microorganisms break down organic matter, releasing methane and carbon dioxide as byproducts.
Applications of Biogas
Biogas can be used as a fuel for cooking, heating, and electricity generation. It can also be upgraded to natural gas quality and used as a vehicle fuel or injected into the natural gas grid. Additionally, the organic byproduct of anaerobic digestion, known as digestate, can be used as a nutrient-rich fertilizer for agricultural crops.
Environmental Benefits of Biogas
Biogas production helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions by capturing methane, a potent greenhouse gas, that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere from decomposing organic waste. It also helps in waste management by providing a sustainable way to treat organic waste materials.
Study Guide
- Define biogas and list its primary components.
- Explain the process of anaerobic digestion and how it leads to biogas production.
- Describe the various applications of biogas as a renewable energy source.
- Discuss the environmental benefits of biogas production.
- Compare the advantages and disadvantages of using biogas as a renewable energy source.
By understanding the process of biogas production and its applications, we can appreciate its significance as a sustainable energy source and its role in promoting environmental sustainability.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Protection, Reproduction and Cooperation
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key