Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis is a vital process in the immune system where certain cells engulf and digest foreign particles such as bacteria, dead cells, and cellular debris. This process helps in protecting the body from infections and maintaining tissue homeostasis.
Mechanism of Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis involves several steps:
- Chemotaxis: Chemical signals attract phagocytic cells to the site of infection or inflammation.
- Adherence: The phagocytic cell attaches to the surface of the foreign particle.
- Ingestion: The cell engulfs the particle, forming a phagosome.
- Phagolysosome Formation: The phagosome fuses with lysosomes, forming a phagolysosome that contains digestive enzymes.
- Digestion: The foreign particle is broken down and digested within the phagolysosome.
- Exocytosis: The indigestible material is expelled from the cell.
Types of Phagocytic Cells
Several types of cells are involved in phagocytosis, including:
- Neutrophils
- Macrophages
- Dendritic cells
- Monocytes
Role in Immunity
Phagocytosis plays a crucial role in the innate immune response by eliminating pathogens and initiating the adaptive immune response. It also helps in tissue repair and removal of cellular debris.
Disorders Related to Phagocytosis
Immunodeficiency disorders, autoimmune diseases, and chronic inflammatory conditions can be associated with dysregulation of phagocytosis.
Study Tips
To effectively study phagocytosis, consider the following tips:
- Understand the sequential steps involved in phagocytosis.
- Learn the types of phagocytic cells and their functions.
- Explore the role of phagocytosis in immunity and disease.
- Use visual aids such as diagrams and animations to visualize the process of phagocytosis.
- Practice identifying the key components and events in phagocytosis.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Solids, liquids and gases
Study Guide Solids, liquids and gases
Solids, liquids and gases  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson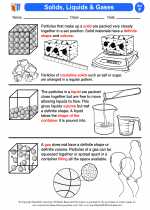 Solids, Liquids & Gases
Solids, Liquids & Gases  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Solids, liquids and gases
Solids, liquids and gases  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Solids, liquids and gases
Solids, liquids and gases  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Solids, liquids and gases
Solids, liquids and gases  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Solids, liquids and gases
Solids, liquids and gases  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Solids, liquids and gases
Solids, liquids and gases 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
Energy
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
Plan an investigation to determine the relationships among the energy transferred, the type of matter, the mass, and the change in the average kinetic energy of the particles as measured by the temperature of the sample.