Aggression
Aggression is a complex behavior that can be observed in both humans and animals. It can be defined as any form of behavior that is intended to cause harm or injury to another living being. Aggression can be physical, such as hitting or pushing, or verbal, such as yelling or insulting. It can also be directed towards others or towards oneself, in the form of self-harm.
Types of Aggression
There are several different types of aggression:
- Physical Aggression: This involves physical actions intended to cause harm, such as hitting, kicking, or biting.
- Verbal Aggression: This involves the use of words or tone of voice to cause harm, such as yelling, insulting, or threatening.
- Relational Aggression: This involves behaviors aimed at damaging someone’s social relationships or social status, such as spreading rumors or excluding someone from a group.
Causes of Aggression
Aggressive behavior can be influenced by a variety of factors, including biological, social, and environmental factors. Some potential causes of aggression include:
- Genetics and brain chemistry
- Family dynamics and parenting style
- Social and cultural influences
- Exposure to violence or trauma
Effects of Aggression
Aggression can have a range of negative effects on individuals and society, including:
- Physical injury or harm
- Emotional and psychological trauma
- Damage to relationships and social connections
- Legal and societal consequences
Managing Aggression
There are various strategies for managing and reducing aggressive behavior, including:
- Developing empathy and emotional regulation skills
- Improving communication and conflict resolution skills
- Seeking professional help and therapy
- Creating a supportive and non-violent environment
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember about aggression:
- Define aggression and identify the different types of aggression.
- Discuss the potential causes of aggression, including biological, social, and environmental factors.
- Explain the effects of aggression on individuals and society.
- Describe strategies for managing and reducing aggressive behavior.
Understanding aggression and its underlying causes can help individuals and communities work towards creating a more peaceful and understanding society.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Cell Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson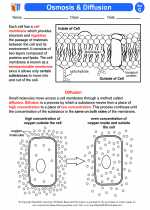
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
