Nitrification
Nitrification is the biological oxidation of ammonia (NH3) or ammonium (NH4+) to nitrite (NO2-) and then to nitrate (NO3-) by two different groups of microorganisms called nitrifying bacteria.
Key Points to Remember
- Nitrification is a two-step process involving the conversion of ammonia to nitrite and then to nitrate.
- Nitrifying bacteria are responsible for carrying out the nitrification process in the soil and aquatic environments.
- The main nitrifying bacteria involved are Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter.
- Nitrification is an important step in the nitrogen cycle, making nitrogen available to plants in the form of nitrate.
Factors Affecting Nitrification
Several factors can affect the rate of nitrification:
- Temperature: Nitrification rates increase with higher temperatures within a certain range.
- pH: Nitrification is favored in neutral to slightly alkaline conditions (pH 6.5-8.5).
- Oxygen: Nitrification is an aerobic process and requires sufficient oxygen for the nitrifying bacteria to function optimally.
- Presence of nitrifying bacteria: The abundance of nitrifying bacteria in the environment directly influences the rate of nitrification.
Importance of Nitrification
Nitrification plays a crucial role in the nitrogen cycle and nutrient availability for plants. The conversion of ammonia to nitrate through nitrification makes nitrogen accessible for plant uptake, contributing to plant growth and ecosystem productivity.
Study Tips
When studying nitrification, it is important to understand the specific steps involved, the key microorganisms responsible, and the environmental factors influencing the process. Be sure to review the significance of nitrification in the context of the nitrogen cycle and its impact on plant nutrition.
Summary
Nitrification is a vital process in the nitrogen cycle, involving the conversion of ammonia to nitrite and then to nitrate by nitrifying bacteria. Understanding the factors influencing nitrification and its significance for plant growth is essential for a comprehensive grasp of ecosystem dynamics.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Cell Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson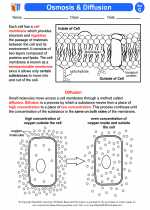
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
