Aquatic Ecosystems
An aquatic ecosystem is a community of organisms and the physical environment in which they live, which is primarily composed of water. There are two main types of aquatic ecosystems: freshwater ecosystems and marine ecosystems.
Freshwater Ecosystems
Freshwater ecosystems include rivers, lakes, ponds, and wetlands. These ecosystems are home to a wide variety of plants and animals, including fish, amphibians, insects, and birds. They are usually rich in nutrients and support diverse food webs.
Marine Ecosystems
Marine ecosystems encompass oceans, coral reefs, estuaries, and coastal areas. They are home to a vast array of marine life, including fish, whales, dolphins, sharks, and various types of plants and algae. Marine ecosystems are vital for regulating the Earth's climate and supporting global biodiversity.
Key Concepts to Study
- Types of aquatic ecosystems
- Adaptations of aquatic organisms
- Food webs and trophic levels in aquatic ecosystems
- Human impacts on aquatic ecosystems
- Conservation and management of aquatic ecosystems
Study Tips
- Review the differences between freshwater and marine ecosystems.
- Learn about the unique adaptations of aquatic organisms, such as gills for breathing underwater and buoyancy control.
- Understand the flow of energy through aquatic food webs and the roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers.
- Explore the various human activities that impact aquatic ecosystems, such as pollution, overfishing, and habitat destruction.
- Research conservation strategies and management practices aimed at protecting and restoring aquatic ecosystems.
By understanding the fundamental principles of aquatic ecosystems, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationships between organisms and their watery environments.
[Aquatic] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Cell Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson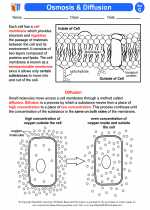
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
