Organ Systems
In the human body, organ systems are groups of organs that work together to perform specific functions. There are 11 major organ systems in the human body, each with its own unique set of organs and functions.
1. Circulatory System
Organs: heart, blood vessels, blood
Function: transports oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells; removes waste products
2. Respiratory System
Function: takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide from the body
3. Digestive System
Organs: mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines
Function: breaks down food and absorbs nutrients
4. Nervous System
Organs: brain, spinal cord, nerves
Function: controls and coordinates body activities; responds to internal and external stimuli
5. Skeletal System
Organs: bones, cartilage, ligaments
Function: provides support and protection for the body; allows movement
6. Muscular System
Function: enables movement; maintains posture and generates heat
7. Excretory System
Organs: kidneys, bladder, ureters, urethra
Function: removes waste products from the body
8. Integumentary System
Function: protects the body from external damage; regulates body temperature
9. Endocrine System
Organs: pituitary gland, thyroid gland, pancreas
Function: regulates body functions through the secretion of hormones
10. Immune System
Organs: spleen, thymus, lymph nodes
Function: defends the body against pathogens and foreign substances
11. Reproductive System
Organs: ovaries, testes, uterus
Function: produces and carries offspring
Study Guide
- What are the organs of the circulatory system and their functions?
- Describe the function of the respiratory system.
- List the organs of the digestive system and explain their role in the process of digestion.
- How does the nervous system control and coordinate body activities?
- Discuss the functions of the skeletal system and its importance in supporting the body.
- Explain the role of the muscular system in enabling movement and maintaining posture.
- Identify the organs of the excretory system and their function in removing waste products from the body.
- What are the functions of the integumentary system in protecting the body?
- Describe the role of the endocrine system in regulating body functions.
- Discuss the function of the immune system in defending the body against pathogens.
- Explain the reproductive system and its role in the production of offspring.
[Organ Systems] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Cell Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson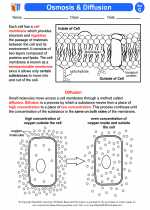
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
