Somatic Nervous System
The somatic nervous system is a component of the peripheral nervous system that is responsible for the voluntary control of body movements and the reception of external stimuli. It enables the brain to receive sensory information from the body and to send motor commands to the skeletal muscles, allowing for conscious and voluntary actions.
Anatomy of the Somatic Nervous System
The somatic nervous system consists of a network of nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) to the muscles and sensory receptors throughout the body. These nerves are known as somatic nerves and are composed of motor neurons that carry signals from the brain to the muscles, and sensory neurons that transmit information from the body to the brain.
Function of the Somatic Nervous System
The primary function of the somatic nervous system is to facilitate voluntary movement and response to external stimuli. When you decide to move your arm, for example, the somatic nervous system transmits signals from the motor cortex of the brain to the muscles in the arm, causing them to contract and produce the desired movement. Additionally, the somatic nervous system is involved in the perception of sensory stimuli such as touch, temperature, and pain, allowing the brain to process and respond to the environment.
Study Guide
- Describe the anatomy of the somatic nervous system.
- Explain the function of the somatic nervous system.
- Differentiate between motor neurons and sensory neurons in the somatic nervous system.
- Provide examples of voluntary actions controlled by the somatic nervous system.
- Discuss the role of the somatic nervous system in sensory perception.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Cell Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson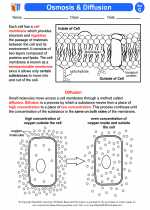
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
