Lithosphere
The lithosphere is the outermost solid shell of the Earth. It is composed of the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle. The lithosphere is divided into several tectonic plates that float and move on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them.
Composition
The lithosphere is primarily composed of rocks, minerals, and soil. The crust is made up of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks, while the upper mantle consists of solid, but flowing, rock materials.
Structure
The lithosphere is divided into several tectonic plates, which can be continental or oceanic in nature. These plates interact with each other at their boundaries, leading to various geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain formation.
Functions
The lithosphere plays a crucial role in supporting life on Earth. It provides a solid surface for the existence of ecosystems, and its geological processes, such as the carbon cycle, influence the planet's climate and atmosphere.
Study Guide
- What is the lithosphere?
- What are the primary components of the lithosphere?
- How is the lithosphere structured?
- What role does the lithosphere play in supporting life on Earth?
- How do tectonic plates interact with each other?
[Lithosphere] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Earthquakes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson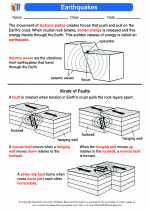
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
