Nervous System
The nervous system is a complex network of nerves and cells that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It is responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities, including movement, sensation, and thought processes.
Anatomy of the Nervous System
The nervous system is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- Central Nervous System (CNS): This includes the brain and spinal cord. The brain is the control center of the body, while the spinal cord serves as a pathway for transmitting information between the brain and the rest of the body.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): This consists of the nerves that extend from the CNS to the rest of the body. The PNS is further divided into the somatic nervous system (voluntary control of body movements) and the autonomic nervous system (involuntary control of functions such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing).
Functions of the Nervous System
The nervous system performs several essential functions, including:
- Receiving sensory input: The nervous system receives information from the body's internal and external environment through sensory receptors.
- Integrating information: The brain processes and interprets sensory information, allowing for appropriate responses.
- Initiating motor output: The nervous system sends signals to muscles and glands to produce physical responses.
- Regulating homeostasis: The autonomic nervous system helps maintain internal balance by controlling functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature.
Study Guide
Here are some key concepts to focus on when studying the nervous system:
- Identify the main components of the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
- Understand the functions of the CNS and PNS, as well as the divisions within the PNS.
- Learn about the structure and function of neurons, the basic building blocks of the nervous system.
- Explore the role of neurotransmitters in transmitting signals between neurons.
- Examine the different regions of the brain and their specific functions, such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
- Understand the importance of the autonomic nervous system in controlling involuntary bodily functions.
By mastering these concepts, you will develop a solid understanding of the nervous system and its significance in maintaining overall bodily function.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics
Study Guide Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson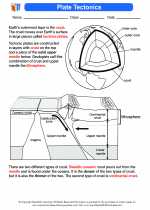 Plate Tectonics
Plate Tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
