Sunlight
Sunlight is the primary source of energy for life on Earth. It is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is emitted by the Sun. Sunlight is essential for various biological and ecological processes, including photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants and other organisms convert sunlight into chemical energy.
Properties of Sunlight
Sunlight consists of a spectrum of wavelengths, ranging from ultraviolet (UV) radiation to visible light and infrared radiation. The visible spectrum of sunlight is the range of wavelengths that can be detected by the human eye, and it includes the colors of the rainbow: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Effects of Sunlight
Sunlight has several important effects on Earth's environment and living organisms. These effects include:
- Photosynthesis: Sunlight is essential for the process of photosynthesis, which is carried out by plants, algae, and some bacteria. During photosynthesis, these organisms use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (sugar) and oxygen.
- Vitamin D synthesis: Sunlight exposure on the skin triggers the production of vitamin D, which is important for bone health and immune function.
- Regulation of circadian rhythms: Sunlight helps regulate the body's internal clock and sleep-wake cycles.
- Heating of the Earth's surface: Sunlight warms the Earth's surface, influencing weather patterns and climate.
- UV radiation: Sunlight includes ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which can have both beneficial and harmful effects on living organisms. UV radiation is essential for the production of vitamin D, but overexposure to UV radiation can damage skin cells and lead to skin cancer.
Measurement of Sunlight
Sunlight is measured using instruments such as solar photometers, pyranometers, and spectroradiometers. These devices quantify the intensity and spectrum of sunlight, providing valuable data for scientific research and applications in fields such as solar energy production and climate studies.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember about sunlight:
- Describe the properties of sunlight, including its spectrum of wavelengths and the visible colors of light.
- Explain the biological and ecological importance of sunlight, focusing on its role in photosynthesis and its effects on living organisms.
- Discuss the effects of sunlight on vitamin D synthesis and circadian rhythms.
- Describe the measurement of sunlight using specialized instruments.
- Discuss the potential benefits and risks of UV radiation present in sunlight.
Understanding the properties and effects of sunlight is essential for grasping its significance in the natural world and its impact on human life and the environment.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson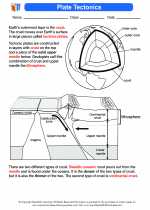
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
