Hexagon
A hexagon is a polygon with six sides and six angles. The sum of the interior angles of a hexagon is always 720 degrees.
Each side of a hexagon is of equal length, and each angle measures 120 degrees in a regular hexagon.
A regular hexagon has six lines of symmetry, meaning it can be divided into six equal parts by drawing lines from each vertex to the opposite vertex.
Some real-life examples of hexagons include the cells of a honeycomb, the shape of a stop sign, and the structure of some snowflakes.
In geometry, hexagons are used to create tessellations, which are a pattern of shapes that fit perfectly together without any gaps.
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. Skip Counting
Study Guide Skip Counting
Skip Counting  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson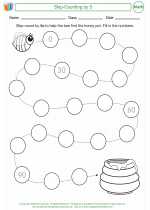 Skip-Counting by 5
Skip-Counting by 5  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson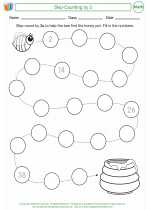 Skip-Counting by 2
Skip-Counting by 2  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Skip Counting
Skip Counting  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Skip Counting
Skip Counting  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Skip Counting
Skip Counting 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
Number and Operations (NCTM)
Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number systems.
Count with understanding and recognize 'how many' in sets of objects.
Develop a sense of whole numbers and represent and use them in flexible ways, including relating, composing, and decomposing numbers.
Connect number words and numerals to the quantities they represent, using various physical models and representations.