Coins Study Guide
Introduction to Coins
Coins are a form of currency used in many countries around the world. They come in different denominations and are used to make purchases, pay for services, and as a form of saving.
Types of Coins
There are several common denominations of coins, including:
- 1 cent (penny)
- 5 cents (nickel)
- 10 cents (dime)
- 25 cents (quarter)
- 50 cents (half-dollar)
- 1 dollar (dollar coin)
Identifying Coins
Each coin has distinct characteristics to help identify them:
- Penny: It is a small, copper-colored coin with Abraham Lincoln's portrait on the front.
- Nickel: A slightly larger coin with a silver color and features a portrait of Thomas Jefferson.
- Dime: The smallest and thinnest coin, it has a silver color and features Franklin D. Roosevelt.
- Quarter: Larger than the dime, it has a silver color and features George Washington.
- Half-dollar: A larger, silver-colored coin with President John F. Kennedy's portrait.
- Dollar coin: Slightly larger than a quarter, it comes in various designs, such as the Sacagawea or Susan B. Anthony dollar.
Value of Coins
Each coin has an assigned value:
- Penny: 1 cent
- Nickel: 5 cents
- Dime: 10 cents
- Quarter: 25 cents
- Half-dollar: 50 cents
- Dollar coin: 1 dollar
Using Coins
Coins are used to make exact change and can be combined to represent different amounts. Understanding their values is important for everyday transactions.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of coins, their values, and how to identify them is an important skill for managing money and making transactions.
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Lines and Angles
Study Guide Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles  Study Guide
Study Guide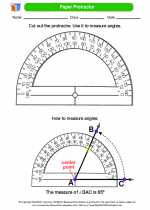 Paper Protractor
Paper Protractor  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson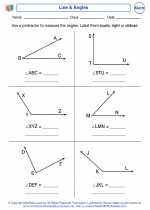 Line & Angles
Line & Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key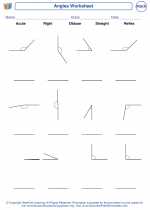 Angles
Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Angles
Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Naming Angles
Naming Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key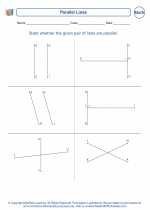 Identifying Parallel Lines
Identifying Parallel Lines  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Identifying Parallel Lines
Identifying Parallel Lines  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Identifying Perpendicular Lines
Identifying Perpendicular Lines  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Lines
Lines  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Lines
Lines  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles 

 Study Guide
Study Guide
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
Geometry (NCTM)
Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships.
Identify, compare, and analyze attributes of two- and three-dimensional shapes and develop vocabulary to describe the attributes.
Connections to the Grade 4 Focal Points (NCTM)
Measurement: As part of understanding two-dimensional shapes, students measure and classify angles.