Types of Regular Patterns:
- Number Patterns: These are sequences of numbers that follow a specific rule or operation. For example, the sequence 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 follows the pattern of adding 2 to the previous number.
- Geometric Patterns: These patterns involve shapes and their arrangements. For instance, a sequence of squares arranged in a row with increasing side lengths forms a geometric pattern.
- Repeating Patterns: These are sequences of elements that cycle or repeat in a consistent manner. For example, a sequence of red, blue, green, red, blue, green forms a repeating pattern.
Identifying Regular Patterns:
- Look for a consistent rule or operation that applies to each element in the sequence.
- Observe the relationship between consecutive elements to determine the pattern.
- Visualize the pattern by creating diagrams or using manipulatives to see the arrangement of elements.
Practicing Regular Patterns:
- Complete number sequences to practice identifying number patterns.
- Create your own geometric patterns using shapes and colors.
- Explore real-life examples of repeating patterns in nature, art, and everyday objects.
Why Regular Patterns are Important:
Understanding regular patterns in math helps develop problem-solving skills, logical reasoning, and critical thinking. These skills are essential for success in various areas of mathematics and in real-world applications.
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Lines and Angles
Study Guide Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles  Study Guide
Study Guide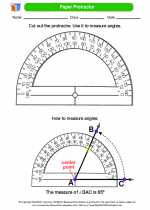 Paper Protractor
Paper Protractor  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson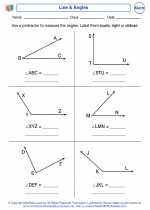 Line & Angles
Line & Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key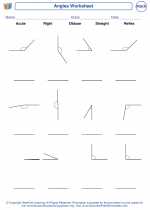 Angles
Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Angles
Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Naming Angles
Naming Angles  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key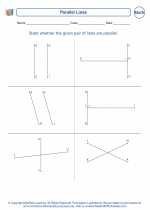 Identifying Parallel Lines
Identifying Parallel Lines  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Identifying Parallel Lines
Identifying Parallel Lines  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Identifying Perpendicular Lines
Identifying Perpendicular Lines  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Lines
Lines  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Lines
Lines  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Lines and Angles
Lines and Angles 

 Study Guide
Study Guide
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
Geometry (NCTM)
Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships.
Identify, compare, and analyze attributes of two- and three-dimensional shapes and develop vocabulary to describe the attributes.
Connections to the Grade 4 Focal Points (NCTM)
Measurement: As part of understanding two-dimensional shapes, students measure and classify angles.