Pressure Study Guide
Definition: Pressure is the amount of force applied to a given area.
Units of Pressure:
There are several units of pressure, including:
- Pascals (Pa)
- Atmospheres (atm)
- Pounds per square inch (psi)
- Millimeters of mercury (mmHg) or Torr
Formula for Pressure:
The formula for pressure is:
Pressure = Force / Area
Factors Affecting Pressure:
Several factors affect pressure, including:
- Force applied
- Area over which the force is applied
- Depth (in the case of fluid pressure)
Applications of Pressure:
Pressure has numerous applications in everyday life, including:
- Weather systems and atmospheric pressure
- Hydraulic systems
- Blood pressure in the human body
- Scuba diving and the effects of water pressure
Pressure in Fluids:
When a force is applied to a fluid, it creates pressure. The pressure exerted by a fluid depends on its density and the depth of the fluid.
Study Tips:
When studying pressure, it's helpful to:
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Money
Study Guide Money
Money  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson How Much Change?
How Much Change?  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson Garage Sale
Garage Sale  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson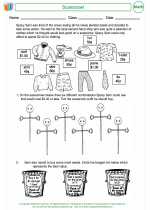 Scarecrow!
Scarecrow!  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Money
Money  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Money
Money  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Money
Money  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Money
Money  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Money
Money  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Money
Money  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Money
Money 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key

Create And Print more Money worksheets with Money Skills Worksheets generator
The resources above cover the following skills:
Algebra (NCTM)
Use mathematical models to represent and understand quantitative relationships.
Model problem situations with objects and use representations such as graphs, tables, and equations to draw conclusions.