Math Problems Study Guide
Understanding Math Problems
Math problems are questions that require mathematical operations to solve. These problems can involve a variety of mathematical concepts such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, fractions, decimals, percentages, and more.
Types of Math Problems
There are different types of math problems including word problems, equations, inequalities, and geometry problems. Word problems are written in the form of a story and require you to identify the mathematical operations needed to solve them. Equations involve finding the value of an unknown variable, while inequalities involve finding the range of values for a variable. Geometry problems involve shapes, angles, and measurements.
Steps for Solving Math Problems
- Read the problem carefully: Understand what the problem is asking and identify key information.
- Identify the mathematical operations: Determine which operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) are needed to solve the problem.
- Set up the equation or problem: Write out the equation or problem based on the information given.
- Solve the problem: Perform the necessary operations to find the solution.
- Check your answer: Verify that your solution makes sense and answers the question.
Tips for Solving Math Problems
Here are some tips for effectively solving math problems:
- Practice working with different types of problems to improve your problem-solving skills.
- Break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts.
- Use visual aids or diagrams to help understand and solve geometry problems.
- Double-check your work and verify your answers to avoid mistakes.
Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems to help you improve your math problem-solving skills:
1. Solve the following equation for x: 3x + 5 = 172. A recipe calls for 2 1/2 cups of flour, but you only have 1 3/4 cups. How much more flour do you need?
3. If a shirt originally costs $40 and is now on sale for 25% off, what is the sale price?
4. A rectangular garden has a length of 12 meters and a width of 8 meters. What is the area of the garden?
Conclusion
By understanding the different types of math problems, following a systematic approach to solving them, and practicing regularly, you can improve your math problem-solving skills and become more confident in tackling a variety of mathematical challenges.
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Fifth Grade. Angles

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key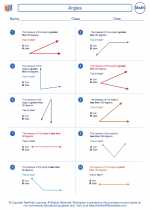
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key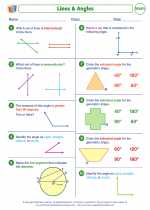
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key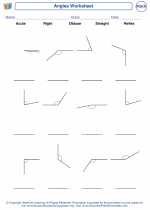
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
