Slant Height
Slant height is a term commonly used in geometry, especially when dealing with 3-dimensional shapes such as cones and pyramids. It refers to the distance from the base to the apex (top) of the shape along its slanting side.
Calculating Slant Height
The slant height of a cone or pyramid can be calculated using the Pythagorean Theorem. If the height (h) and the radius of the base (r) are known, the slant height (l) can be found using the formula:
l = √(r2 + h2)
Example
Let's say we have a cone with a radius of 5 units and a height of 12 units. To find the slant height, we can use the formula:
l = √(52 + 122)
l = √(25 + 144)
l = √169
l = 13 units
Study Guide
- Understand the concept of slant height and its significance in 3-dimensional geometry.
- Learn the Pythagorean Theorem and how it is used to calculate the slant height of cones and pyramids.
- Practice using the formula l = √(r2 + h2) to find the slant height in different examples.
- Understand the relationship between the slant height, height, and radius of the base in cones and pyramids.
◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Finding Volume
Study Guide Finding Volume
Finding Volume  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson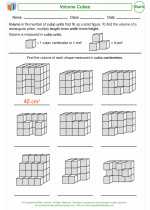 Volume Cubes
Volume Cubes  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson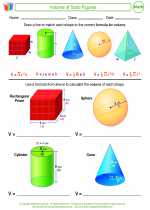 Volume of Solid Figures
Volume of Solid Figures  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson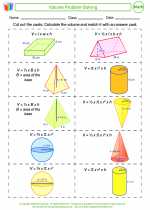 Volume Problem
Volume Problem  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Finding Volume
Finding Volume  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Finding Volume
Finding Volume  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Finding Volume
Finding Volume  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Finding Volume
Finding Volume 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
Geometry (NCTM)
Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships.
Precisely describe, classify, and understand relationships among types of two- and three-dimensional objects using their defining properties.
Use visualization, spatial reasoning, and geometric modeling to solve problems.
Use geometric models to represent and explain numerical and algebraic relationships.
Measurement (NCTM)
Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements.
Select and apply techniques and tools to accurately find length, area, volume, and angle measures to appropriate levels of precision.
Develop strategies to determine the surface area and volume of selected prisms, pyramids, and cylinders.