Infectious Agents
Let's explore the fascinating world of infectious agents! Infectious agents are microorganisms that can cause disease in their host organisms. These agents include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Understanding these agents is crucial for preventing and treating infectious diseases.
Bacteria
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that can be found almost everywhere. While some bacteria are beneficial and essential for life, others can cause diseases such as strep throat, tuberculosis, and urinary tract infections. Bacteria can be treated with antibiotics, but overuse of antibiotics has led to the rise of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria.
Viruses
Viruses are tiny infectious agents that can only replicate inside the cells of another organism. They cause diseases such as the flu, common cold, HIV/AIDS, and COVID-19. Vaccines are crucial in preventing viral infections, as they train the immune system to recognize and fight specific viruses.
Fungi
Fungi are a diverse group of organisms that include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. While many fungi are harmless, some can cause infections such as athlete's foot, ringworm, and yeast infections. Antifungal medications are used to treat fungal infections.
Parasites
Parasites are organisms that live on or inside another organism and benefit at the host's expense. They can cause a wide range of diseases, including malaria, giardiasis, and parasitic worms. Parasitic infections are often treated with antiparasitic medications.
Study Guide
- What are infectious agents?
- Explain the role of bacteria in causing diseases.
- How do viruses replicate and cause diseases?
- Give examples of fungal infections and their treatments.
- What are parasites, and how do they cause diseases?
- Describe the methods used to treat parasitic infections.
Understanding infectious agents is essential for preventing the spread of diseases and developing effective treatments. By studying these microorganisms, scientists and healthcare professionals can work towards improving global public health.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food webs/food chains

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson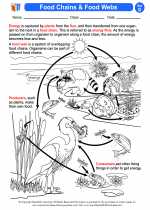
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
