Volcanic Gases
Volcanic gases are emitted during volcanic eruptions and are composed of a variety of gases, including water vapor, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and other trace gases. These gases are released from the magma as it rises to the surface and can have significant effects on the environment and climate.
Composition of Volcanic Gases
The composition of volcanic gases varies depending on the type of volcano and the stage of the eruption. The primary gases released during volcanic eruptions include:
- Water Vapor (H2O): This is the most abundant gas released during volcanic eruptions.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): This is a greenhouse gas that can contribute to climate change when released in large quantities.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): This gas can react with water vapor in the atmosphere to produce acid rain, which can have detrimental effects on the environment.
- Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S): This gas has a characteristic "rotten egg" smell and can be toxic in high concentrations.
- Trace Gases: Other gases such as carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and various halogen compounds can also be released during volcanic eruptions.
Effects of Volcanic Gases
Volcanic gases can have a range of effects on the environment, climate, and human health. Some of the key effects include:
- Climate Change: The release of large amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases can contribute to global warming and climate change.
- Acid Rain: Sulfur dioxide emissions can lead to the formation of acid rain, which can harm plants, aquatic ecosystems, and infrastructure.
- Air Quality: Volcanic gases can reduce air quality and pose health risks to humans and animals, particularly in the vicinity of the eruption.
- Atmospheric Chemistry: The release of trace gases can affect the chemical composition of the atmosphere, leading to complex interactions and potential impacts on ozone depletion and air pollution.
Study Guide
To study the topic of volcanic gases, it's important to understand the composition of volcanic gases, their effects on the environment and climate, and the potential hazards they pose to human health. Here are some key points to focus on:
- What are the primary gases released during volcanic eruptions?
- How do volcanic gases contribute to climate change?
- What is the impact of sulfur dioxide emissions on the environment?
- How can volcanic gases affect air quality and human health?
- What are some of the potential long-term effects of volcanic gas emissions on the atmosphere?
Additionally, it's important to study specific case studies of volcanic eruptions and their associated gas emissions, as well as the monitoring and mitigation strategies used to assess and mitigate the impacts of volcanic gases.
By understanding the composition and effects of volcanic gases, we can better appreciate the complex interactions between volcanoes and the Earth's atmosphere, and work towards managing the potential hazards associated with volcanic activity.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food webs/food chains

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson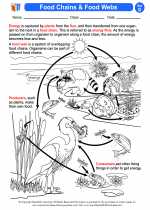
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
