Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding is the process by which two or more atoms are joined together to form a compound. There are three main types of chemical bonding: ionic bonding, covalent bonding, and metallic bonding.
Ionic Bonding
In ionic bonding, electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions. These ions are then attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, forming an ionic bond.
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding occurs when atoms share electrons to achieve a more stable electron configuration. This sharing of electrons creates a bond between the atoms, holding them together in a molecule.
Metallic Bonding
Metallic bonding is found in metals and involves the delocalized sharing of electrons among a lattice of metal atoms. This sharing of electrons allows metals to conduct electricity and heat.
Study Guide
- What is chemical bonding?
- What are the three main types of chemical bonding?
- Explain how ionic bonding occurs.
- Describe the process of covalent bonding.
- What is metallic bonding and where is it found?
[Chemical Bonding] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Genetics - Study of Heredity

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson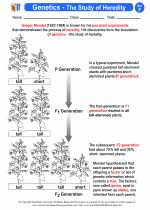
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
