Electrons
Electrons are subatomic particles that orbit the atomic nucleus. They carry a negative charge and are essential for the structure of atoms and the behavior of matter. Here are some key points to understand about electrons:
- Charge: Electrons carry a negative charge, which is equal in magnitude to the positive charge of protons. This negative charge allows electrons to be attracted to the positively charged nucleus of an atom.
- Location: Electrons are located in atomic orbitals, which are regions of space surrounding the nucleus where electrons are likely to be found. These orbitals exist in distinct energy levels known as electron shells.
- Behavior: Electrons exhibit both particle-like and wave-like properties, a concept known as wave-particle duality. They can also move between different energy levels by absorbing or emitting photons of light.
- Role in Chemistry: Electrons play a crucial role in chemical bonding, where they are shared or transferred between atoms to form molecules and compounds.
- Electricity: The flow of electrons is responsible for the generation of electric currents, which powers various electrical devices and systems.
Study Guide
To understand electrons more deeply, consider focusing on the following areas:
- Atomic Structure: Learn about the basic structure of an atom, including the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons within the nucleus and electron shells.
- Quantum Mechanics: Explore the principles of quantum mechanics that govern the behavior of electrons, such as Heisenberg's uncertainty principle and the Schrödinger equation.
- Chemical Bonding: Investigate how electrons participate in different types of chemical bonding, including covalent, ionic, and metallic bonding.
- Electricity and Magnetism: Study the role of electrons in electrical conduction and the generation of magnetic fields.
- Applications: Explore real-world applications of electron behavior, such as in semiconductor devices, electron microscopy, and quantum computing.
By delving into these areas, you can develop a comprehensive understanding of electrons and their significance in the world of science and technology.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Introduction to earth science
Study Guide Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson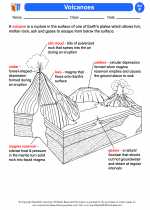 Volcanoes
Volcanoes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE