Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that describes the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic levels. It is a branch of physics that provides a mathematical description of the wave-particle duality of matter and energy.
Key Concepts in Quantum Mechanics:
- Wave-Particle Duality: According to quantum mechanics, particles such as electrons and photons exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior. This means that they can behave as waves and particles depending on the experimental conditions.
- Quantization: Quantum mechanics introduces the concept of quantization, which states that certain physical properties, such as energy and angular momentum, are restricted to discrete, or quantized, values.
- Uncertainty Principle: The uncertainty principle, formulated by Werner Heisenberg, states that the more precisely the position of a particle is known, the less precisely its momentum can be known, and vice versa. This principle places fundamental limits on the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties can be known simultaneously.
- Quantum States and Superposition: Quantum systems can exist in superposition, meaning they can be in multiple states simultaneously. The state of a quantum system is described by a mathematical object called a wave function, which contains information about the probabilities of finding the system in different states.
- Quantum Entanglement: Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon in which the quantum states of two or more particles become linked in such a way that the state of one particle cannot be described independently of the state of the others. This phenomenon has been the subject of extensive study and has implications for quantum computing and cryptography.
Study Guide for Quantum Mechanics:
- What is the wave-particle duality and how does it manifest in quantum mechanics?
- Explain the concept of quantization and provide examples of quantized properties in quantum mechanics.
- Discuss the implications of the uncertainty principle in quantum mechanics and its significance in the study of subatomic particles.
- Describe the concept of quantum states and the phenomenon of superposition in quantum mechanics.
- Explain the concept of quantum entanglement and its potential applications in quantum technologies.
- Provide a brief overview of the historical development of quantum mechanics and its major contributors.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Introduction to earth science
Study Guide Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson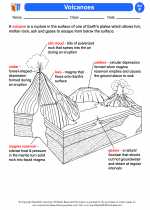 Volcanoes
Volcanoes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE