Eukarya
Eukarya is one of the three domains of life, alongside Bacteria and Archaea. It consists of all organisms that have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles within their cells. This domain includes a wide variety of organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Characteristics of Eukaryotic Organisms
- Presence of a true nucleus containing genetic material
- Membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus
- Complex cellular organization
- Can be unicellular or multicellular
Eukarya Kingdoms
Within the domain Eukarya, organisms are classified into several kingdoms, including:
- Plantae: Consists of multicellular, photosynthetic organisms such as trees, flowers, and grasses.
- Animalia: Comprises multicellular organisms with specialized tissues and organ systems, capable of movement and obtaining energy through consumption of other organisms.
- Fungi: Includes organisms such as mushrooms, yeasts, and molds, which obtain nutrients through absorption and often reproduce through spores.
- Protista: A diverse group of mostly unicellular organisms, including algae, amoebas, and ciliates.
Study Guide
To understand Eukarya and its characteristics, it's important to focus on the following key points:
- What are the defining features of eukaryotic cells?
- How do eukaryotic organisms differ from prokaryotic organisms in terms of cellular structure?
- What are the major kingdoms within the domain Eukarya, and what are the distinguishing characteristics of each?
- Compare and contrast unicellular and multicellular eukaryotic organisms.
- Research a specific organism within the Eukarya domain and present its characteristics, habitat, and ecological role.
Understanding the diversity and complexity of eukaryotic life forms is essential for comprehending the vast array of organisms that inhabit our planet.
[Eukarya] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Introduction to earth science
Study Guide Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson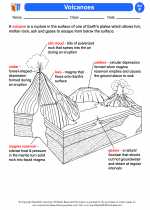 Volcanoes
Volcanoes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Introduction to earth science
Introduction to earth science 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE