Archaeology
Archaeology is the study of human history and prehistory through the excavation and analysis of material culture. It provides a unique perspective on the past by examining artifacts, structures, and other physical remains left by ancient civilizations.
Key Concepts
- Artifacts: Objects created or modified by humans, such as tools, pottery, and jewelry.
- Excavation: The process of carefully uncovering and documenting archaeological sites.
- Stratigraphy: The study of rock layers and the sequence of events they represent.
- Carbon Dating: A method used to determine the age of organic materials by measuring the decay of radioactive carbon isotopes.
- Cultural Anthropology: The study of human cultures and societies, often used in conjunction with archaeology to interpret ancient remains.
Study Tips
- Review the different methods of dating artifacts and sites, such as carbon dating and stratigraphy.
- Understand the role of cultural anthropology in interpreting archaeological finds.
- Practice analyzing and interpreting artifacts to understand the daily lives and practices of ancient peoples.
- Explore case studies of famous archaeological discoveries to gain insights into the field.
- Visit local museums or archaeological sites to see real-life examples of artifacts and excavation techniques.
Further Reading
For further exploration of archaeology, consider reading the following books:
- "Archaeology: Theories, Methods, and Practice" by Colin Renfrew and Paul Bahn
- "Archaeology" by Kelly L. Lueth
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Our Solar System
Study Guide Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson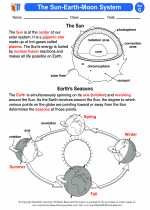 The Sun-Earth-Moon System
The Sun-Earth-Moon System  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
