Earth's Core
The Earth's core is the innermost part of our planet. It is divided into two layers: the outer core and the inner core. The core is primarily composed of iron and nickel, with smaller amounts of other elements.
Outer Core
The outer core is a liquid layer that surrounds the inner core. It is about 2,200 kilometers thick and is responsible for generating Earth's magnetic field through the movement of molten iron and nickel.
Inner Core
The inner core is a solid sphere with a radius of about 1,220 kilometers. It experiences extremely high temperatures and pressures, causing the iron and nickel to exist in a solid state despite the intense heat.
Study Guide
- What are the two layers of the Earth's core?
- What are the primary elements that make up the core?
- What is the outer core responsible for?
- Describe the state of matter in the inner core.
- What factors contribute to the high temperatures and pressures in the inner core?
[Earth's Core] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Our Solar System
Study Guide Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson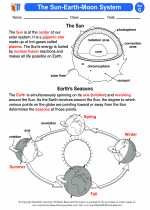 The Sun-Earth-Moon System
The Sun-Earth-Moon System  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
