Our Solar System -> eukaryotic
Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells are one of the two major cell types, the other being prokaryotic cells. They are characterized by the presence of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells:
- Nucleus: Contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and is surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
- Membrane-bound Organelles: Eukaryotic cells contain various specialized structures such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and others.
- Complex Structure: Eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells.
- Cellular Organization: Eukaryotic cells exhibit compartmentalization, allowing different cellular processes to occur in specific organelles.
Examples of Eukaryotic Organisms:
Eukaryotic cells are found in a wide variety of organisms, including:
Study Guide:
Here are some key points to remember about eukaryotic cells:
- What is the defining feature of eukaryotic cells?
Answer: The presence of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. - List three examples of eukaryotic organisms.
Answer: Plants, animals, and fungi. - How do eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotic cells?
Answer: Eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, and contain membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and organelles. - Name two membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells and describe their functions.
Answer: Mitochondria (site of cellular respiration) and endoplasmic reticulum (involved in protein and lipid synthesis).
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Our Solar System
Study Guide Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson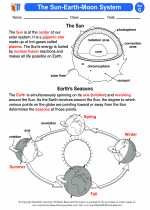 The Sun-Earth-Moon System
The Sun-Earth-Moon System  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
