Exosphere
The exosphere is the outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere. It begins at the exobase, which is located at the top of the thermosphere, and extends into outer space. This region is where the Earth's atmosphere merges with space, and it is composed of very low-density gases, such as hydrogen and helium, along with some heavier molecules like oxygen and nitrogen.
Key Points to Remember:
- The exosphere is the outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere.
- It begins at the exobase, located at the top of the thermosphere, and extends into outer space.
- The exosphere is composed of very low-density gases, such as hydrogen and helium, along with some heavier molecules like oxygen and nitrogen.
Study Guide Questions:
- Where does the exosphere begin?
- What are the main gases found in the exosphere?
- What is the exobase?
[Exosphere] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Our Solar System
Study Guide Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson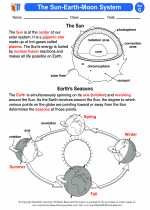 The Sun-Earth-Moon System
The Sun-Earth-Moon System  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
