Genes
Genes are the basic units of heredity in living organisms. They are made up of DNA and serve as the instructions for building and maintaining an organism. Genes determine various traits, such as eye color, height, and susceptibility to certain diseases. They are passed down from parents to offspring through the process of reproduction.
Structure of Genes
Genes are composed of sequences of DNA, which are made up of four nucleotide bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases form pairs (A with T, and C with G) and are organized into a double helix structure. The specific sequence of these bases in a gene determines the specific instructions it contains.
Functions of Genes
Genes encode the information needed for the synthesis of proteins, which are essential for the structure and function of cells. They also play a role in regulating various biological processes, such as growth, development, and metabolism. Additionally, genes can undergo mutations, which can lead to changes in the traits they control.
Study Guide
- Define genes and explain their role in heredity.
- Describe the structure of genes, including the composition of DNA and the arrangement of nucleotide bases.
- Discuss the functions of genes, including their role in protein synthesis and biological regulation.
- Explain how genes can undergo mutations and the potential impact of these mutations on traits.
- Discuss the inheritance of genes from parents to offspring and the concept of dominant and recessive traits.
Understanding genes is crucial in the field of genetics and has implications for various areas of science, including medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Our Solar System

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson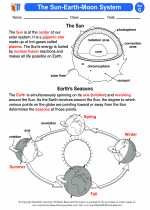
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
