Reflect
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. This phenomenon is commonly observed with light, sound, and water waves.
Types of Reflection
There are two main types of reflection: specular reflection and diffuse reflection.
- Specular Reflection: This type of reflection occurs when light or other waves are reflected in a single direction, such as the reflection of light off a smooth mirror surface.
- Diffuse Reflection: Diffuse reflection occurs when light or other waves are reflected in many different directions, such as the reflection of light off a rough or uneven surface.
Law of Reflection
The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. This means that the angle at which a wave strikes a surface is equal to the angle at which it reflects off the surface.
Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
θi = θr
Where θi is the angle of incidence and θr is the angle of reflection.
Applications of Reflection
Reflection has numerous practical applications in everyday life and in various fields of science and technology. Some common examples include:
- Use of mirrors for reflection of light in optical devices
- Reflection of sound waves in architectural acoustics
- Use of reflective surfaces in solar panels to capture and concentrate sunlight
- Utilization of reflective materials in road signs and safety clothing for increased visibility
Study Guide
When studying the topic of reflection, it is important to understand the difference between specular and diffuse reflection, as well as the law of reflection. Make sure to practice applying the law of reflection to solve problems involving the reflection of light or other waves off various surfaces. Additionally, explore real-world examples of reflection and its applications to gain a deeper understanding of the concept.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Our Solar System

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson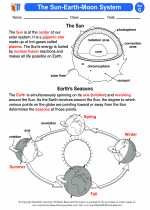
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
