Terrestrial Ecosystems
Terrestrial ecosystems are land-based ecosystems that encompass a variety of habitats including forests, grasslands, deserts, and tundras. These ecosystems are shaped by factors such as climate, soil, topography, and vegetation, and are home to a diverse array of plant and animal species.
Key Concepts
- Climate: The prevailing weather conditions in a region, including temperature, precipitation, and humidity, that influence the type of terrestrial ecosystem found in that area.
- Soil: The composition and quality of soil affect the types of plants that can grow in a terrestrial ecosystem and influence the overall health of the ecosystem.
- Vegetation: The plant life in a terrestrial ecosystem, which varies based on factors such as climate, soil, and water availability.
- Animal Adaptations: Animals in terrestrial ecosystems have developed a range of adaptations to survive in their specific habitats, including camouflage, burrowing, and specialized feeding behaviors.
- Human Impact: Human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, and pollution, have a significant impact on terrestrial ecosystems and their biodiversity.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to focus on while studying terrestrial ecosystems:
- Describe the different types of terrestrial ecosystems and the unique characteristics of each (forests, grasslands, deserts, tundras).
- Explain the factors that influence the distribution and characteristics of terrestrial ecosystems, such as climate, soil, and vegetation.
- Discuss the relationships between plants and animals within terrestrial ecosystems and how they have adapted to their environments.
- Analyze the impact of human activities on terrestrial ecosystems and propose potential solutions to mitigate their effects.
- Compare and contrast the biodiversity and ecological dynamics of different terrestrial ecosystems.
Understanding terrestrial ecosystems is crucial for understanding the Earth's overall biodiversity and the impact of human activities on natural environments. Be sure to study the interactions between abiotic and biotic factors in terrestrial ecosystems and how these relationships contribute to the overall balance of these diverse habitats.
[Terrestrial] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Our Solar System
Study Guide Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson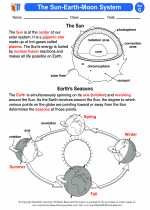 The Sun-Earth-Moon System
The Sun-Earth-Moon System  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Our Solar System
Our Solar System 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
