Liquid Waste
Liquid waste refers to any discarded, untreated liquid substances that may be harmful to the environment or human health. This can include wastewater from households, industrial processes, agriculture, and other sources. Liquid waste can contain a variety of contaminants, including chemicals, pathogens, and organic matter, which can pollute water sources and ecosystems if not properly managed and treated.
Sources of Liquid Waste
- Household wastewater from sinks, showers, toilets, and laundry
- Industrial effluents from manufacturing processes
- Agricultural runoff from farms and livestock operations
- Mining and construction site drainage
- Stormwater from urban areas
Impacts of Liquid Waste
Improper disposal of liquid waste can lead to a range of environmental and health problems, including:
- Water pollution
- Contamination of soil and groundwater
- Threats to aquatic ecosystems and wildlife
- Spread of waterborne diseases
- Adverse effects on human health
Management and Treatment
Proper management and treatment of liquid waste are essential to minimize its negative impacts. This can involve:
- Wastewater treatment plants for urban and industrial effluents
- Septic systems for household wastewater in rural areas
- Regulations and enforcement to prevent illegal dumping and pollution
- Public education and awareness about responsible waste disposal
Study Guide
Key Concepts
- Definition of liquid waste
- Sources of liquid waste
- Impacts of improper liquid waste disposal
- Methods for managing and treating liquid waste
Study Questions
- What are the sources of liquid waste?
- How does improper liquid waste disposal impact the environment and human health?
- What are the methods used to manage and treat liquid waste?
- Why is it important to properly dispose of liquid waste?
Activities
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. The Endocrine system and Reproduction
Study Guide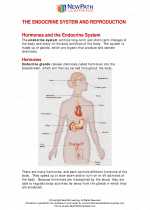 The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key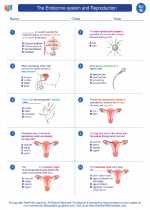 The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key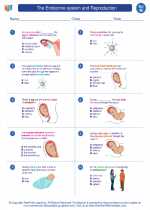 The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key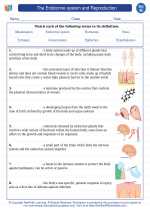 The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
