Pongo: The Genus of Orangutans
The genus Pongo refers to the group of great apes known as orangutans. Orangutans are native to the rainforests of Indonesia and Malaysia and are known for their distinctive red or reddish-brown fur. There are three species of orangutans within the genus Pongo: the Bornean orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus), the Sumatran orangutan (Pongo abelii), and the recently identified Tapanuli orangutan (Pongo tapanuliensis).
Physical Characteristics
Orangutans are characterized by their long arms and a highly dexterous, hook-shaped hand which is well-adapted for gripping tree branches. They are also known for their remarkable intelligence and are considered one of the most intelligent primates.
Behavior and Habitat
Orangutans are primarily arboreal, spending most of their time in the trees of the tropical rainforests. They are solitary animals, with adult males having large home ranges that overlap with the smaller ranges of several females. Orangutans are also known for their use of tools, such as sticks for extracting insects or as a tool for defense.
Conservation Status
Unfortunately, orangutans are listed as critically endangered due to habitat loss, poaching, and the illegal pet trade. Conservation efforts are underway to protect their remaining habitats and to rehabilitate and reintroduce orphaned and displaced orangutans back into the wild.
Study Guide
- What are the three species of orangutans within the genus Pongo? Answer: Bornean orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus), Sumatran orangutan (Pongo abelii), and Tapanuli orangutan (Pongo tapanuliensis).
- Describe the physical characteristics of orangutans. Answer: Orangutans have long arms, red or reddish-brown fur, and highly dexterous, hook-shaped hands.
- What is the conservation status of orangutans? Answer: Orangutans are critically endangered due to habitat loss, poaching, and the illegal pet trade.
By understanding the genus Pongo and the species within it, we can appreciate the unique characteristics and the conservation challenges facing these incredible primates.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. The Endocrine system and Reproduction
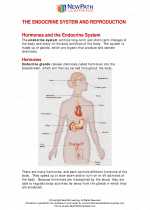
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key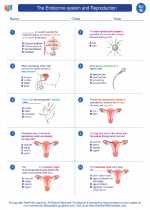
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key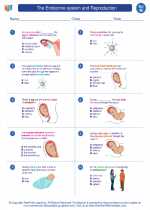
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key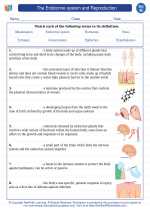
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
