Quantitative Observation
Quantitative observation refers to the process of collecting and analyzing data that is numerical in nature. It involves using measurable and objective data to describe and quantify phenomena. This type of observation is crucial in scientific research and provides a way to gather empirical evidence and draw conclusions based on numerical data.
Examples of Quantitative Observation
Quantitative observation can be applied to various scientific fields, including:
- Physics: Measuring the velocity of an object in motion
- Chemistry: Determining the temperature at which a substance undergoes a phase change
- Biology: Counting the number of organisms in a population
- Geology: Measuring the depth of a rock layer
Collecting Quantitative Data
To make quantitative observations, it is important to:
- Use precise and accurate measuring instruments, such as rulers, thermometers, and balances.
- Record data consistently using standardized units of measurement (e.g., meters, grams, seconds).
- Repeat observations to ensure reliability and minimize errors.
Analysis of Quantitative Data
Once quantitative data is collected, it can be analyzed using statistical methods such as:
- Calculating averages and measures of central tendency (e.g., mean, median, mode).
- Identifying patterns and trends through graphical representations (e.g., line graphs, bar charts).
- Assessing relationships between different variables using correlation and regression analysis.
Study Guide
To effectively study quantitative observation, consider the following key points:
- Understand the difference between quantitative and qualitative observations.
- Practice using measuring instruments and recording data with precision.
- Learn to analyze quantitative data using statistical tools and methods.
- Explore real-world examples of quantitative observation in different scientific disciplines.
- Engage in hands-on experiments and activities that involve making quantitative observations.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. The Endocrine system and Reproduction
Study Guide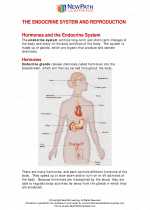 The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key The endocrine system and Reproduction
The endocrine system and Reproduction 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
