What are Trophic Levels?
Trophic levels are the hierarchical levels in an ecosystem, each representing a different level of energy transfer. They categorize organisms based on their feeding behavior and position in the food chain.
The Different Trophic Levels
There are typically four main trophic levels in a food chain:
- Primary Producers (Autotrophs): These are organisms, such as plants, algae, and some bacteria, that can produce their own energy through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
- Primary Consumers (Herbivores): These are organisms that consume the primary producers. They are typically herbivores that feed directly on plants or algae.
- Secondary Consumers (Carnivores): These are organisms that consume the primary consumers. They are carnivores that feed on herbivores.
- Tertiary Consumers (Top Predators): These are organisms that consume the secondary consumers. They are often at the top of the food chain and are carnivores that have few or no predators of their own.
Energy Transfer in Trophic Levels
As energy moves through the trophic levels, it is transferred from one level to the next. However, each transfer is not 100% efficient, and much of the energy is lost as heat. This phenomenon is known as the 10% rule, where only about 10% of the energy is passed on to the next trophic level, while the rest is lost. This is why there are typically fewer top predators in an ecosystem compared to primary producers.
Study Guide for Trophic Levels
When studying trophic levels, it's essential to understand the following key points:
- The definition of trophic levels and their role in energy transfer.
- The types of organisms found at each trophic level and their feeding behaviors.
- The concept of the 10% rule and its implications for energy flow in ecosystems.
- How disruptions in trophic levels can impact an ecosystem, such as the consequences of overhunting top predators or changes in primary producer populations.
Understanding trophic levels is vital for comprehending the dynamics of ecosystems and the interconnectedness of organisms within them.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. The Endocrine system and Reproduction
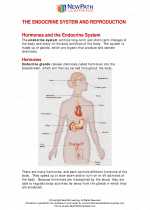
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key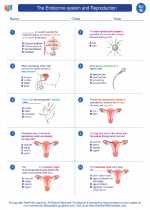
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key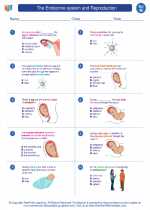
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key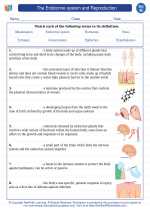
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
