Weather Forecasts
Weather forecasts are predictions about the future state of the atmosphere. Meteorologists use a variety of tools and data to make these predictions, including information from weather satellites, radar systems, weather stations, and computer models. By analyzing current weather patterns and using historical data, meteorologists can make educated guesses about what the weather will be like in the coming hours, days, and even weeks.
Key Concepts
- Weather Variables: Meteorologists consider several key variables when making weather forecasts, including temperature, humidity, wind speed and direction, air pressure, and precipitation.
- Weather Maps: Maps are used to display and analyze weather data, such as temperature, precipitation, and pressure. These maps help meteorologists identify weather patterns and make predictions.
- Forecasting Tools: Meteorologists use various tools, such as weather satellites, radar, and computer models, to gather and analyze data for making forecasts.
- Accuracy and Limitations: Weather forecasts are based on complex models and historical data, but they are not always 100% accurate. Meteorologists work to improve the accuracy of forecasts, but there are limitations due to the chaotic nature of the atmosphere.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to focus on when studying weather forecasts:
- Understand the different weather variables and how they impact the overall forecast.
- Learn to read and interpret weather maps, including understanding symbols and patterns.
- Explore the various tools and technologies used in weather forecasting, and how they contribute to making predictions.
- Consider the factors that can affect the accuracy of weather forecasts, such as the limitations of current technology and the complexity of the atmosphere.
By understanding these key concepts and studying the relevant tools and techniques, you can gain a better understanding of how weather forecasts are made and improve your ability to interpret and use weather forecasts in your daily life.
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Fifth Grade. Congruent Shapes
Study Guide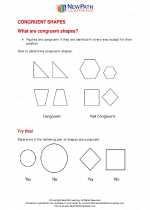 Congruent Shapes
Congruent Shapes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Congruent Shapes
Congruent Shapes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Congruent Shapes
Congruent Shapes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Congruent Shapes
Congruent Shapes 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
Geometry (NCTM)
Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships.
Identify, compare, and analyze attributes of two- and three-dimensional shapes and develop vocabulary to describe the attributes.
Explore congruence and similarity.