Combustion Reactions
Combustion reactions are chemical reactions that involve the rapid combination of a substance with oxygen, resulting in the release of heat and light. These reactions are commonly associated with the burning of fuels such as wood, coal, and gasoline.
The general chemical equation for a combustion reaction is:
Fuel + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Heat + Light
For example, the combustion of methane (CH4) can be represented by the following equation:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + Heat + Light
During a combustion reaction, the fuel undergoes oxidation, producing carbon dioxide and water as the primary products. The release of heat and light is a result of the exothermic nature of the reaction.
Factors Affecting Combustion Reactions
Several factors can influence the rate and efficiency of combustion reactions, including:
- Availability of oxygen: Combustion reactions require a sufficient supply of oxygen to proceed. Limited oxygen can result in incomplete combustion, leading to the formation of carbon monoxide and soot.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures generally promote faster combustion reactions by providing the necessary activation energy for the reaction to occur.
- Fuel composition: The chemical composition of the fuel can affect the combustion process. For example, fuels with higher carbon content tend to produce more carbon dioxide during combustion.
- Surface area: Finely divided or powdered forms of fuel have a larger surface area, which can lead to faster combustion due to increased contact with oxygen.
Applications of Combustion Reactions
Combustion reactions have numerous practical applications, including:
- Power generation in steam turbines and internal combustion engines
- Heating and cooking processes
- Industrial processes such as metallurgy and glass manufacturing
- Combustion-based propulsion systems in vehicles and aircraft
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember about combustion reactions:
- Define combustion reaction and identify its general chemical equation.
- Explain the role of oxygen in combustion reactions and its impact on the products formed.
- Discuss the factors that influence the rate and efficiency of combustion reactions, including availability of oxygen, temperature, fuel composition, and surface area.
- Describe the practical applications of combustion reactions in everyday life and various industries.
Understanding combustion reactions is essential for comprehending the processes involved in energy production, environmental impact, and the functioning of many technological systems.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food webs/food chains

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson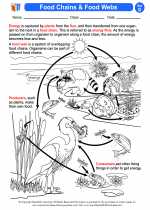
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
