Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the study of the structure, function, and interactions of the molecules that make up living organisms. This field encompasses the study of DNA, RNA, proteins, and other macromolecules essential for life. Understanding molecular biology is crucial for comprehending the fundamental processes of life, such as replication, transcription, translation, and gene expression.
Key Concepts in Molecular Biology
- DNA Structure and Function: DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material that contains the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms. Understanding the double helix structure of DNA and its role in encoding genetic information is fundamental to molecular biology.
- RNA and Protein Synthesis: RNA, or ribonucleic acid, plays a crucial role in protein synthesis. The process involves transcription, where the genetic information from DNA is transcribed into RNA, and translation, where the information in RNA is used to produce proteins. These processes are essential for the expression of genetic information.
- Genetic Regulation and Expression: Molecular biology involves the study of how genes are regulated and expressed in living organisms. This includes understanding the mechanisms that control gene activity, such as epigenetic modifications and gene regulatory networks.
- Recombinant DNA Technology: This area of molecular biology focuses on the manipulation of DNA molecules to create recombinant DNA that can be used for various purposes, such as the production of genetically modified organisms, gene therapy, and the development of biotechnological products.
- Biological Macromolecules: Molecular biology also encompasses the study of biological macromolecules, including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, and their roles in cellular structure, function, and metabolism.
Study Guide
To effectively study molecular biology, it is essential to grasp the following concepts:
- Understand the structure and function of DNA, including the double helix structure, base pairing, and the genetic code.
- Comprehend the processes of transcription and translation, and how they are essential for protein synthesis.
- Learn about gene regulation and expression, including the role of transcription factors, epigenetic modifications, and gene regulatory networks.
- Explore the applications of recombinant DNA technology and its significance in biotechnology and medicine.
- Master the basics of biological macromolecules and their roles in cellular processes.
Additionally, practicing with molecular biology experiments, analyzing case studies, and staying updated with current research in the field will enhance your understanding of molecular biology.
By mastering the key concepts and staying engaged with the latest developments, you can develop a solid foundation in molecular biology and its significance in the study of life sciences.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Our Solar System

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson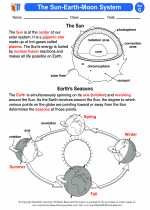
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
