Combined Gas Law
The combined gas law is a gas law that combines Charles's law, Boyle's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. It is used to relate the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas sample when the amount of gas and the number of moles are constant.
Formula
The combined gas law is expressed mathematically as:
(P1 * V1) / T1 = (P2 * V2) / T2
Where:
- P1 and P2 are the initial and final pressures of the gas
- V1 and V2 are the initial and final volumes of the gas
- T1 and T2 are the initial and final temperatures of the gas (in Kelvin)
Usage
The combined gas law is particularly useful when you need to calculate the final pressure, volume, or temperature of a gas when at least one of these properties changes. It allows you to predict the behavior of gases under different conditions and is a fundamental concept in the study of thermodynamics and gas laws.
Sample Problems
Let's look at a couple of sample problems to understand how the combined gas law is applied:
Problem 1: If a gas occupies a volume of 4.0 L at a pressure of 1.0 atm and a temperature of 300 K, what will be its volume if the pressure is increased to 2.0 atm and the temperature is increased to 400 K?
Solution 1:
We can use the combined gas law to solve this problem:
(P1 * V1) / T1 = (P2 * V2) / T2
Plugging in the given values:
(1.0 atm * 4.0 L) / 300 K = (2.0 atm * V2) / 400 K
Solving for V2:
V2 = (1.0 atm * 4.0 L * 400 K) / (300 K * 2.0 atm) = 5.3 L
Therefore, the volume will be 5.3 L when the pressure is increased to 2.0 atm and the temperature is increased to 400 K.
Problem 2: A gas initially occupies a volume of 2.0 L at a pressure of 3.0 atm and a temperature of 400 K. If the volume is reduced to 1.0 L and the temperature is decreased to 300 K, what will be the final pressure of the gas?
Solution 2:
Using the combined gas law:
(P1 * V1) / T1 = (P2 * V2) / T2
Plugging in the given values:
(3.0 atm * 2.0 L) / 400 K = (P2 * 1.0 L) / 300 K
Solving for P2:
P2 = (3.0 atm * 2.0 L * 300 K) / (400 K * 1.0 L) = 2.25 atm
Therefore, the final pressure of the gas will be 2.25 atm when the volume is reduced to 1.0 L and the temperature is decreased to 300 K.
Study Guide
To master the combined gas law, it's essential to understand the individual gas laws that it combines, namely Charles's law, Boyle's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. Additionally, practicing various problems involving changes in pressure, volume, and temperature of gases will strengthen your understanding of this concept. Here are some key points to focus on:
- Understanding the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature in gases
- Converting temperature to Kelvin scale for use in gas law calculations
- Applying the combined gas law to solve problems involving changes in gas properties
- Recognizing the direct and inverse relationships between gas properties
By mastering the combined gas law, you'll be equipped to analyze and predict the behavior of gases in various scenarios, laying a strong foundation for further studies in thermodynamics and gas laws.
Good luck with your studies!
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Our Solar System

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson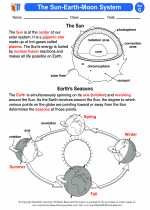
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
